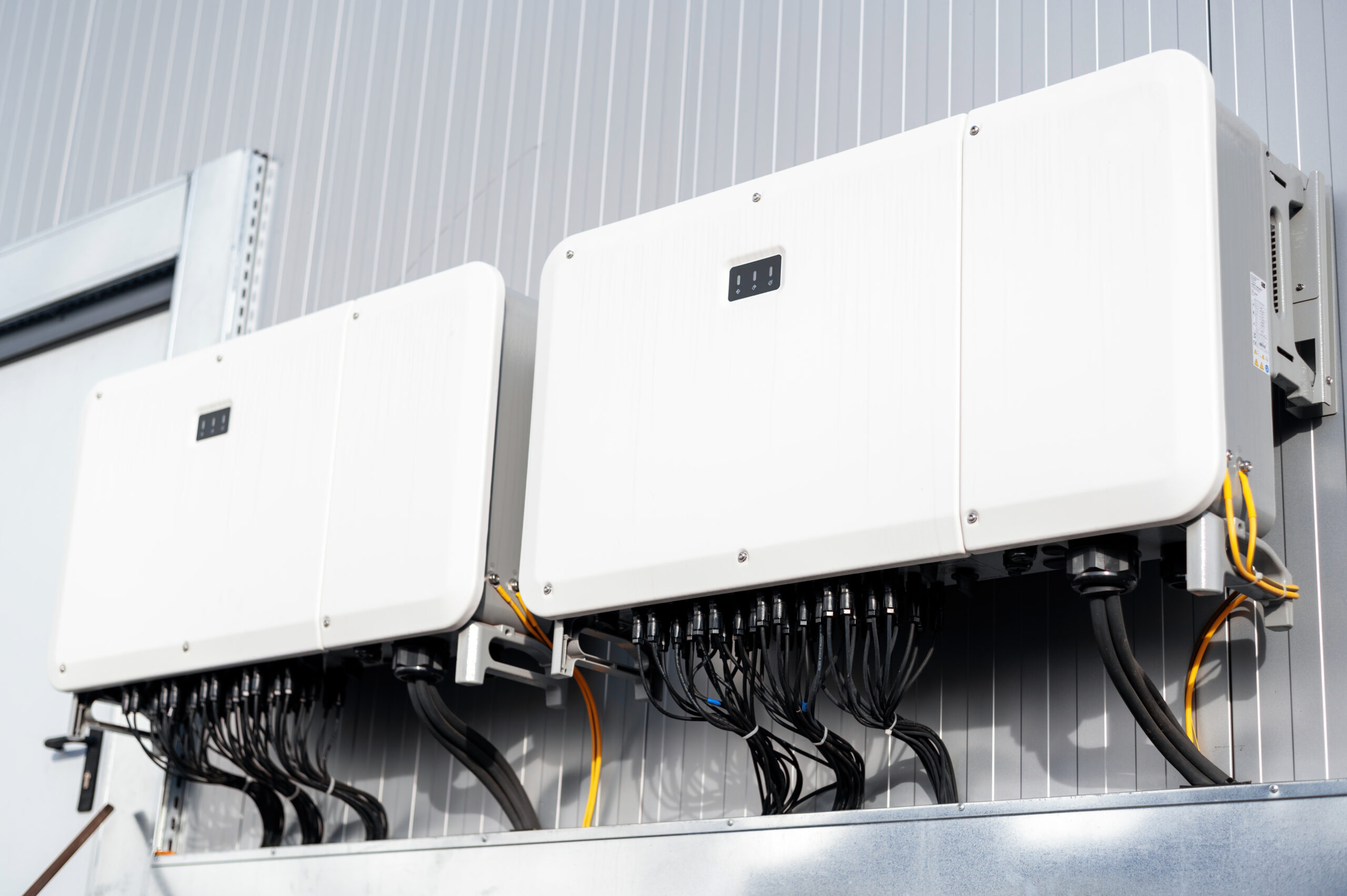
When connecting inverters in parallel, the primary goal is to achieve redundancy and load sharing rather than enhancing efficiency. By linking two inverters together, you can combine their power capacities to support higher total output, but the overall efficiency will depend on various factors, including the inverters’ design and load management. This parallel connection helps distribute the load evenly between the inverters, ensuring a more balanced operation. It’s a great way to maximize the potential of your inverters and make the most out of your power generation setup. Let’s delve deeper into the concept of connecting inverters in parallel for enhanced power output and efficiency!
Preparing for Parallel Connection
When preparing for a parallel connection of inverters, there are a few essential steps to follow to ensure a safe and successful setup:
Ensure Inverters are Compatible for Parallel Connection:
- Check the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to confirm that your inverters are designed to be connected in parallel.
- Look for compatibility in model, voltage, frequency, and power rating.
Check Electrical Compatibility and Safety Requirements:
- Verify that the electrical parameters of both inverters, such as voltage and frequency, match to avoid any issues during the parallel connection.
- Ensure that the electrical system you connect the inverters can handle the combined power output.
- Adhere to safety requirements, such as using appropriate circuit breakers and protective devices.
Gather Necessary Tools and Equipment:
- Ensure you have the tools and equipment for the parallel connection, such as cables, connectors, and wiring accessories.
- Ensure that the wires and connectors are rated to handle your inverters’ current and power levels.
By following these steps, you’ll be well-prepared for connecting your inverters parallel. Prioritizing safety and compatibility is crucial for ensuring optimal performance.
How to Connect 2 Inverters in Parallel
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to connect two inverters in parallel:
Select Compatible Inverters:
- Ensure that both inverters are compatible with parallel connections.
- Check their specifications, including voltage, frequency, and power ratings, to ensure they match.
Install the Inverters:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to install both inverters in their designated locations properly.
- Make sure to provide adequate ventilation and secure mounting for each inverter.
Connect DC Inputs:
- Connect the positive (+) and negative (-) DC terminals of each inverter to the corresponding terminals of the battery bank.
- Use appropriate cables and connectors based on the current and power requirements.
Connect AC Outputs:
- Connect the AC output terminals of both inverters to a standard AC distribution panel or load center.
- Ensure proper wiring and use suitable circuit breakers for protection purposes.
Battery Connections:
- Ensure the battery bank is connected correctly to both inverters, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Double-check the polarity and tighten all connections securely.
Configure the Inverters:
- Access the configuration settings of each inverter and set them to operate in parallel mode.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for configuring the inverters correctly.
Monitoring and Control:
- Set up any monitoring and control systems provided by the inverters to keep track of their performance and status.
- Please familiarize yourself with the monitoring features and ensure they are functioning correctly.
Testing and Commissioning:
- Test the parallel operation of the inverters by applying a load and verifying that both inverters are functioning as expected.
- Monitor the voltage, frequency, and overall performance during the testing phase.
Compliance and Safety:
- Ensure that the parallel connection of the inverters complies with all relevant electrical codes and safety regulations.
- Double-check all connections, grounding, and protective measures to ensure a safe and reliable system.
Remember, it’s essential to consult the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines throughout the process.
Tips and Best Practices
Proper Grounding: Ensure that both inverters are grounded according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and local electrical codes. This helps prevent electrical shocks and ensures the safety of the system.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the performance of both inverters to identify any issues or discrepancies. To keep the inverters operating optimally, perform routine maintenance, such as cleaning or inspecting connections.
Synchronization: Pay attention to the inverters’ synchronization to ensure they are operating in harmony. This involves monitoring the voltage and frequency output of both inverters to ensure they are in sync and providing consistent power.
Protection Devices: Install appropriate protection devices, such as surge protectors and circuit breakers, to safeguard the inverters and the connected equipment from electrical faults or overloads.
Proper Ventilation: Ensure both inverters have adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding clearance and airflow to maintain optimal performance.
Documentation: Record the installation process, configuration settings, and any modifications made. This documentation will be helpful for future reference, troubleshooting, or expanding the system.
Remember, consulting with a professional or an electrician experienced in parallel inverter installations is always recommended to ensure a safe and reliable connection.
Advanced Parallel Connection Techniques
There are some advanced parallel connection techniques for inverters. These techniques go beyond the basic setups and offer more flexibility and control over your solar power system. Here are a few key techniques to consider:
Multiple Inverter Parallel Connection: Instead of connecting just two inverters in parallel, you can expand your system by connecting multiple inverters. This allows for higher power output and the ability to scale your system to meet increasing energy demands.
Parallel Connection with Battery Storage: Integrating battery storage systems with parallel-connected inverters allows you to store excess energy generated by your solar panels. This stored energy can be used during low sunlight or power outages, providing backup power and maximizing self-consumption.
Advanced Monitoring and Control: Implementing advanced monitoring and control strategies enables you to optimize the performance of your parallel-connected inverters. Real-time monitoring of power output, voltage levels, and other parameters allows for proactive management and troubleshooting.
Synchronization Techniques: Synchronization between parallel-connected inverters is crucial for smooth operation. Advanced synchronization techniques like phase and frequency help maintain stability and prevent power imbalances.
These advanced techniques offer greater flexibility, efficiency, and control over your solar power system. Implementing these techniques may require specialized knowledge and expertise. Consulting with professionals or reputable solar energy companies can help ensure a successful implementation.
Future Trends in Parallel Inverter Technology
The future of parallel inverter technology looks incredibly promising. Here are some exciting trends and advancements to look forward to:
Smart Inverters: Smart inverters are becoming increasingly popular due to their advanced communication and control capabilities. These inverters can monitor grid conditions and adjust their output to ensure stability and efficient power delivery. They also enable seamless integration with innovative grid technologies, allowing for better grid-tied parallel operation.
Grid-Tied Parallel Operation: Grid-tied parallel operation is a growing trend that enables multiple inverters to work together to supply power to the grid. This approach enhances system reliability and allows for more efficient energy distribution. It also helps the possibility of selling excess power back to the grid, promoting renewable energy adoption.
Integration with Renewable Energy Storage Systems: As renewable energy storage systems, such as batteries, become more affordable and accessible, parallel inverters are being designed to integrate these systems seamlessly. This integration allows for efficient energy management, maximizing self-consumption and reducing reliance on the grid during peak demand periods.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: The advancements in parallel inverter technology contribute to improved energy efficiency and sustainability. By optimizing power output, enabling grid-tied operation, and integrating with energy storage, these technologies help reduce energy waste, enhance system performance, and support the transition to cleaner and greener energy sources.
These future trends in parallel inverter technology hold great promise for the energy industry. They pave the way for more efficient and sustainable energy systems, empowering individuals and communities to embrace renewable energy and reduce their carbon footprint.
Connecting inverters in parallel is a valuable strategy for maximizing power output and efficiency in renewable energy systems. We expect more innovative solutions and improved compatibility for parallel operations as technology advances. By staying informed about industry developments and best practices, you can optimize the performance of your inverters and contribute to a more sustainable energy environment.